Webhooks
Webhooks deliver real-time notifications when events occur in an Martis account. Instead of polling the API for updates, webhooks push event data to a configured endpoint, enabling immediate response to payment completions, payout status changes, and other critical events. These events are all considered idempotent, so in a batch operation, each event that occurs in that batch consists of one operation.
When an event occurs (e.g., a payment succeeds), Martis sends an HTTP POST request to the configured webhook endpoint with event details in the request body. The receiving server processes the event and returns a 2xx status code to acknowledge receipt.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Event occurs | A payment charge succeeds, a payout completes, etc. |
| Webhook sent | Martis sends a POST request to the registered endpoint |
| Signature verification | The receiving server verifies the request signature |
| Event processing | The server processes the event data |
| Acknowledgment | The server returns a 2xx response |
Configure Webhook Endpoints
Registered endpoints can be viewed, updated, or deleted from the Integrations menu. Each endpoint displays delivery statistics and recent event history. Webhook endpoints must meet the following requirements:
- HTTPS — Only secure endpoints are supported
- POST method — Endpoints must accept POST requests
- JSON content — Request bodies are JSON-formatted
- 2xx response — Return a success status code to acknowledge receipt
Here's a go-to guide to register a webhook endpoint
-
Step 1 — Navigate to Creator Hub → Integration → Webhook Destinations Tab, click New webhook destination
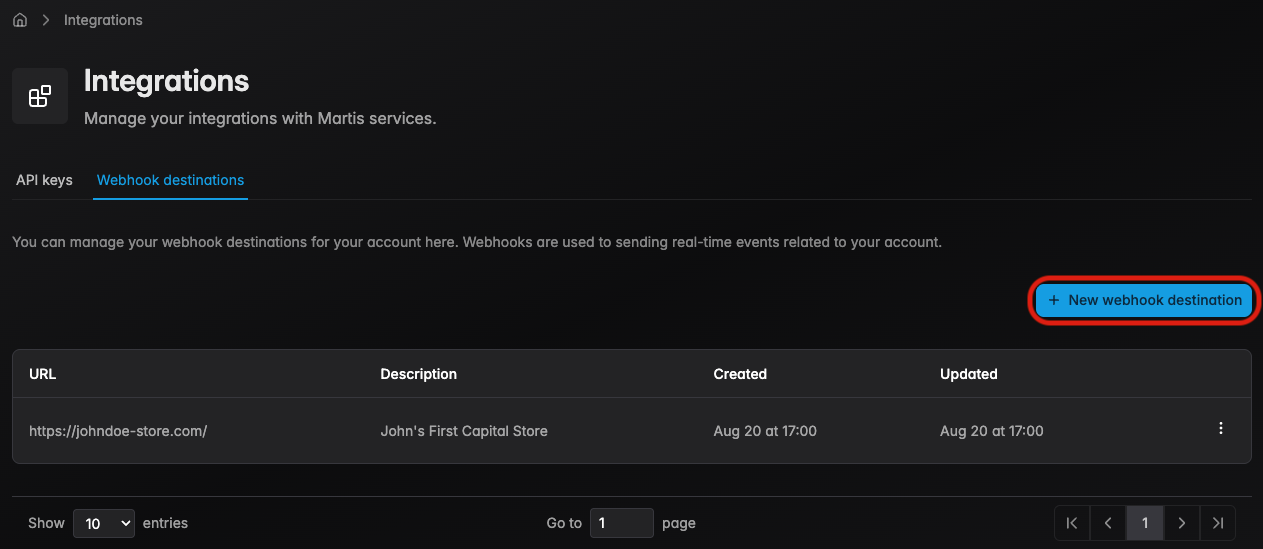
-
Step 2 — Enter a valid HTTPS endpoint URL and an optional description, click Add Webhook
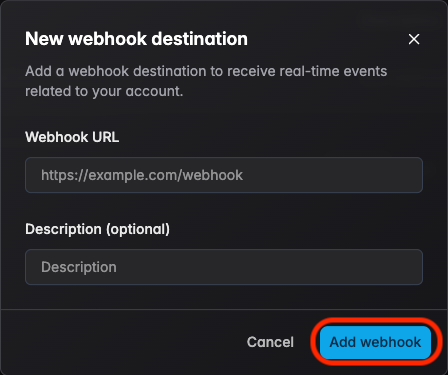
A webhook secret is generated upon creation. Store this secret securely — it is required for signature verification.
Signature Verification
Verify webhook signatures to ensure requests originate from Martis and have not been tampered with.
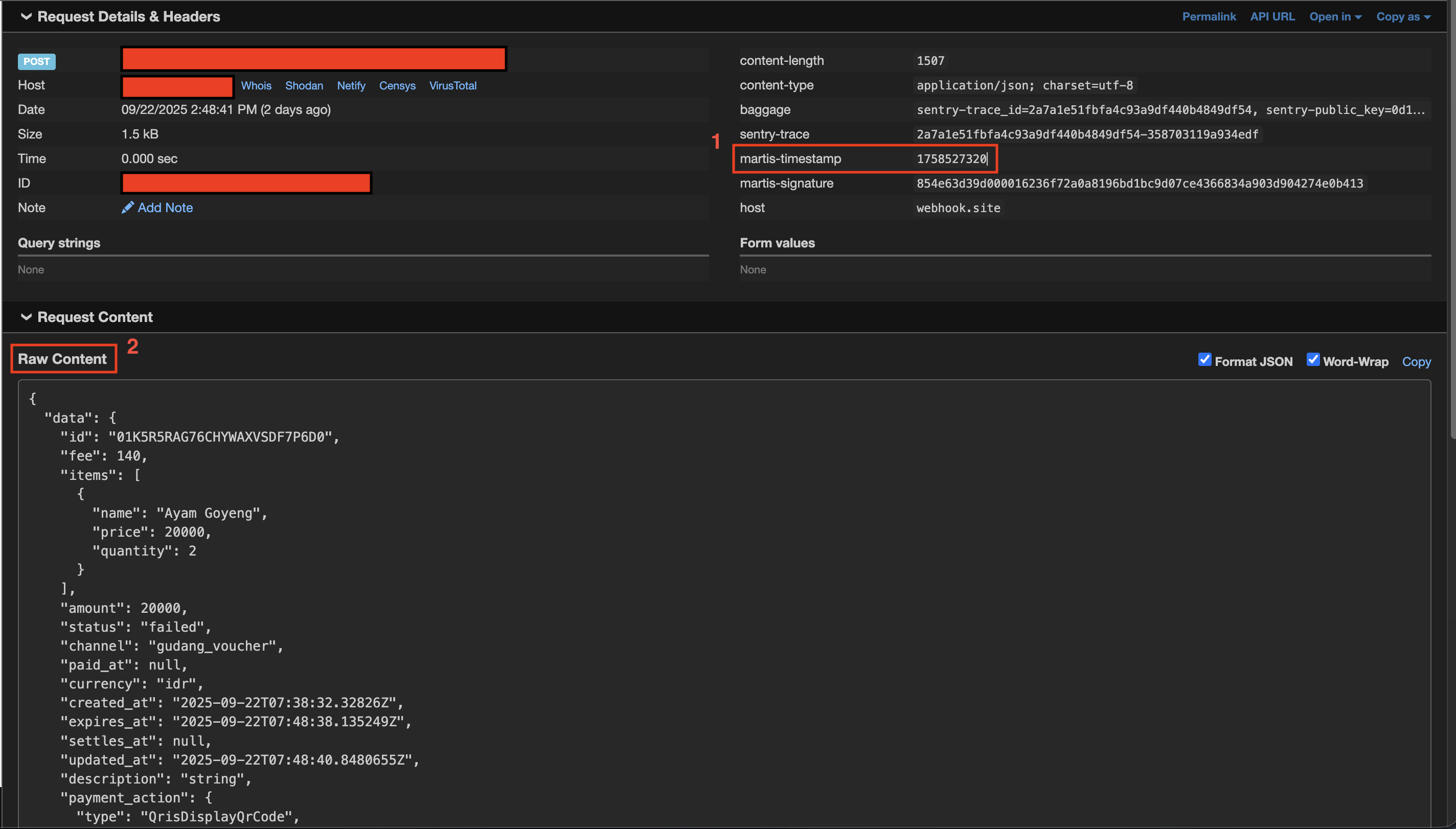
Each webhook request includes two headers for verification:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
{HEADER_TIMESTAMP} | Unix timestamp when the webhook was sent |
{HEADER_SIGNATURE} | HMAC-SHA256 signature of the request |
Verification Process
- Step 1 — Extract the timestamp and signature from request headers
- Step 2 — Construct the signed payload:
{timestamp}.{raw_body} - Step 3 — Compute HMAC-SHA256 using the webhook secret
- Step 4 — Compare the computed signature with the received signature
The request body must be used exactly as received (raw bytes). Do not parse, reformat, or modify the body before computing the signature.
Implementation Examples
Signature Verification
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
public static class WebhookVerification
{
public static bool VerifySignature(
string rawBody,
string timestamp,
string receivedSignature,
string webhookSecret)
{
var payload = $"{timestamp}.{rawBody}";
var expectedSignature = ComputeHmacSha256(payload, webhookSecret);
return CryptographicOperations.FixedTimeEquals(
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(expectedSignature),
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(receivedSignature)
);
}
private static string ComputeHmacSha256(string data, string key)
{
using var hmac = new HMACSHA256(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(key));
var hash = hmac.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(data));
return Convert.ToHexString(hash).ToLower();
}
}
Retry Mechanism
When a webhook delivery fails, Martis automatically retries the request using exponential backoff.
| Attempt | Delay | Cumulative Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immediate | 0 |
| 2 | 5 minutes | 5 minutes |
| 3 | 30 minutes | 35 minutes |
Failure Conditions
A delivery is considered failed when:
- The endpoint returns a non-2xx status code
- The request times out (30 seconds)
- The endpoint is unreachable
After all retry attempts are exhausted, the webhook delivery is marked as failed. Failed events can be viewed in the dashboard and manually retried. To manually request for a retry on failed conditions, you may contact our assigned team.