API Keys
Authenticates requests between servers and Martis's Core API Services. Each key is a unique credential that identifies the requesting application and determines access permissions. Proper key management is essential for maintaining security and preventing unauthorized access.
An API key consists of a secret string that must be included in the Authorization header of every API request. With an existing API key, there are only two configurable properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Descriptive name of the key |
| IP Restrictions | Limits allowed client IP addresses |
An API key provides full authentication access to the Core API services for this account.
Create API Keys
To obtain a secret key for API authentications, please follow these steps:
-
Step 1 — Navigate to Integration → API Keys
-
Step 2 — Click Create API Key
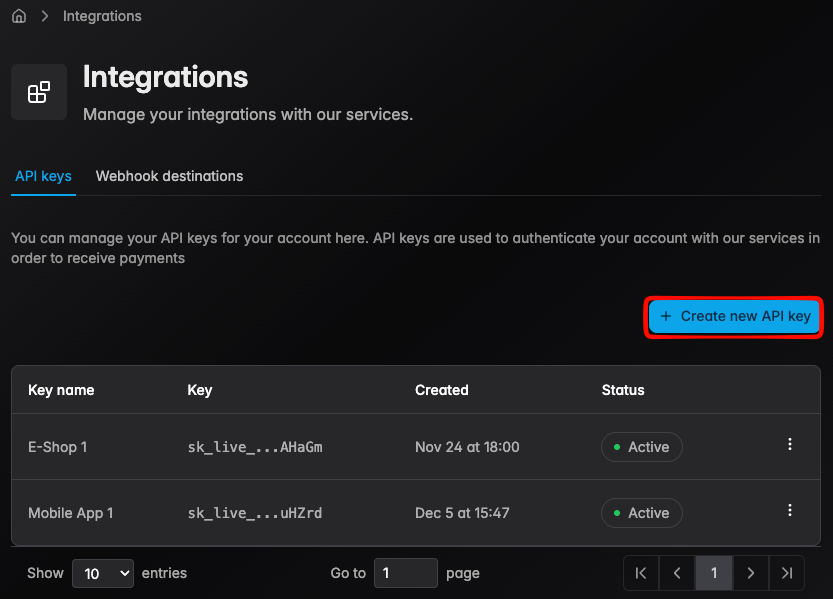
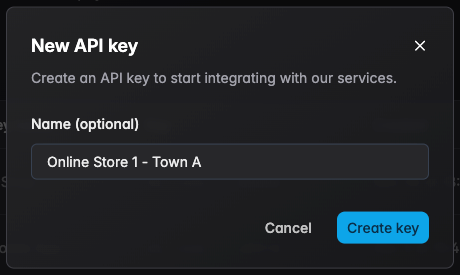
- Step 3 — Enter a name for the key and click Create
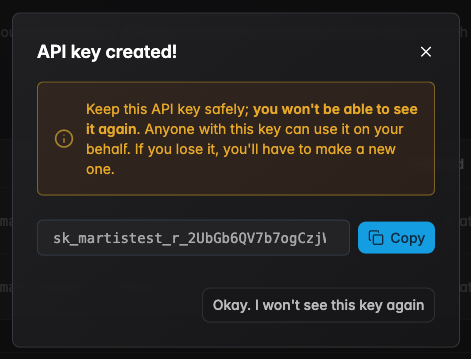
- Step 4 — Copy the secret key and store it securely. Do not share it with anyone!
Storage Best Practices
Think of API keys as sensitive credentials. Below are recommended methods and concrete practices to reduce risk of exposure.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Secret Manager | Fine-grained access control, automatic auditing and encryption at rest |
| Environment Variables | Use injected .env vars from CI/CD, good for server processes and containers |
| Encrypted Configuration | Secrets must be stored with the app; encrypt at rest and restrict file permissions |
- Don't commit keys to source control (inc. forks and branches)
- Don't embed keys in client-side code (browser, mobile, or public bundles)
- Don't paste keys into chat, issue trackers, or forums
- Don't include keys in screenshots or documentation images
- Don't log keys or print them (build or server logs)
- Don't store keys in unencrypted files or public storage (e.g., Public S3)
- Don't reuse one key across multiple environments or services
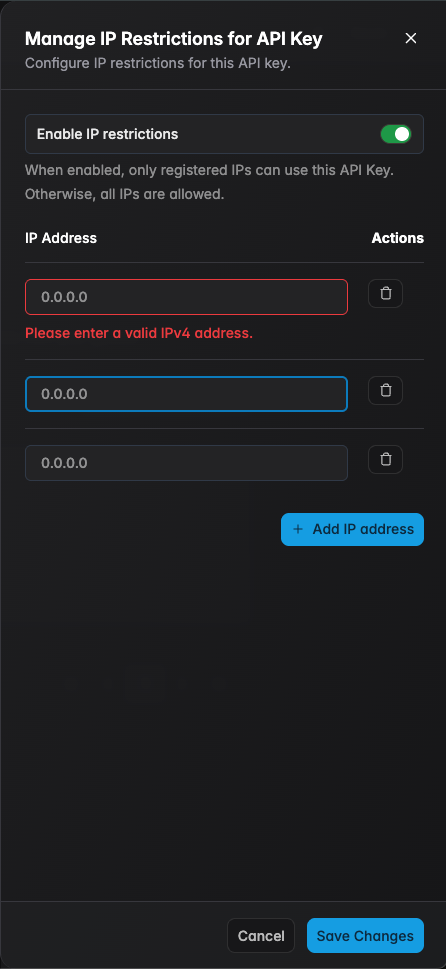
IP Restrictions
Restrict API key usage to specific IP addresses for enhanced security. When enabled, requests from non-listed IP addresses are rejected. To start configuring, please follow these steps:
- Step 2 — Select the key to configure, click Manage IP Restrictions
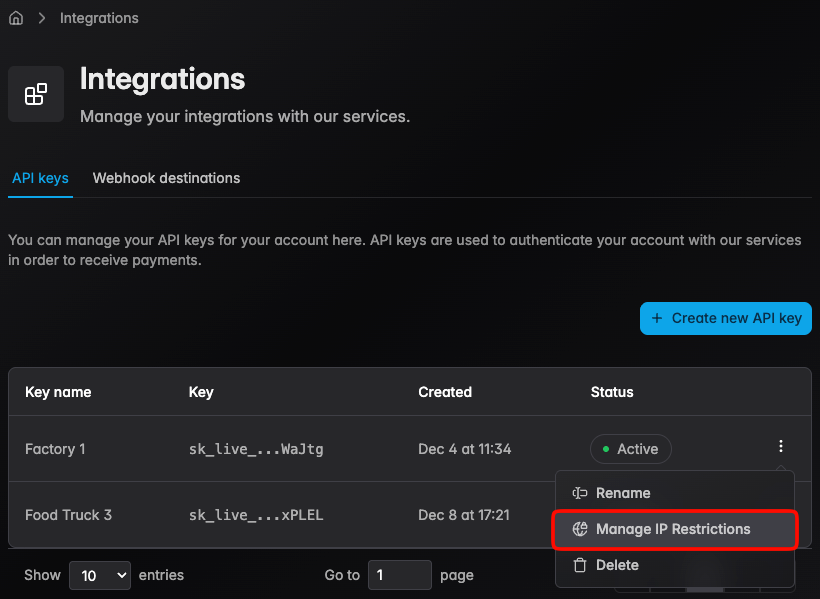
- Step 3 — Enable IP restrictions, and add allowed IP addresses

| Configuration | Allowed IPs | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Unrestricted | Any IP address | Development, internal testing |
| Restricted | Listed IPs only | Production, locked-down environments |
IP restrictions add a security layer but do not replace proper key management. A leaked key from an allowed IP still poses a risk.
Delete Key
Revoked keys immediately prevents all operations provided on the Core API service specified for the account. This action cannot be undone, please follow the previous steps to locate the key that needs to be revoked.
- Step 1 — Click the action button to the specified key needed to be revoked
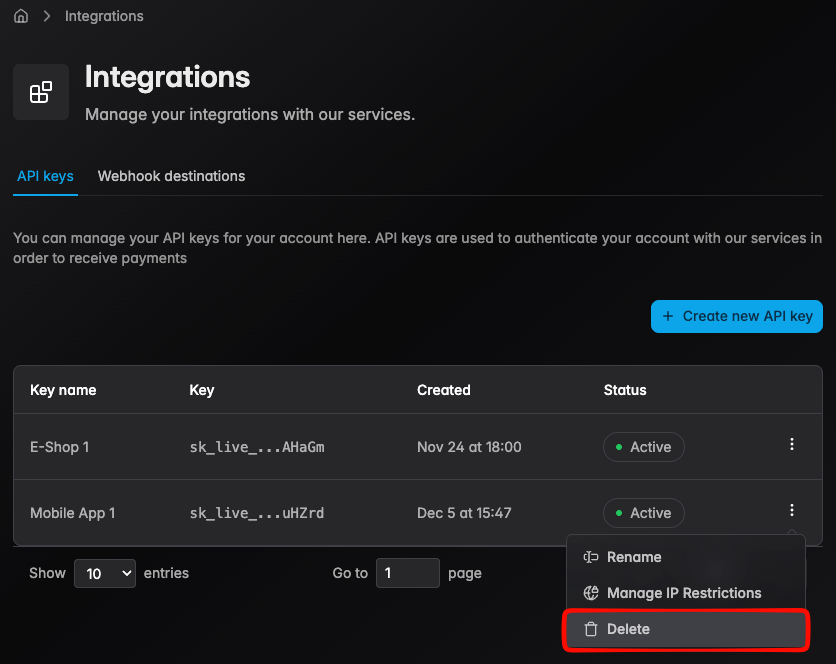
- Step 2 — Confirm the deletion dialog
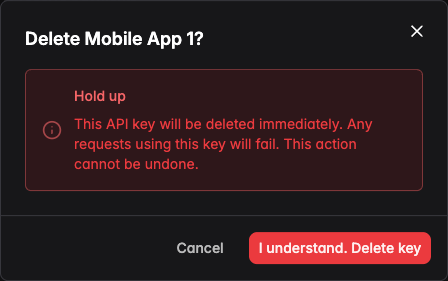
Before revoking a key, ensure no active services depend on it. Revocation causes immediate authentication failures for any requests using that key.
Using API Keys
API keys authenticate and identify your application when calling our APIs. Include the key as a Bearer token in the Authorization header — see the Core Concepts → Authentication section for examples and best practices.